Cryptocurrencies are quite literally a revolution in the way we think about money and finance. At the heart of this revolution are two critical mechanisms that lie therein: proof of work and proof of stake. Both of these systems are responsible for how transactions are validated on a blockchain, ensuring the security of the network. But where exactly do these two differ, and which is the future of crypto?
In this article, we go in-depth into the differences between proof of work and proof of stake. We look at how each system works, the pros and cons of both, and what the future might hold for these two consensus mechanisms.
What is Proof of Work?
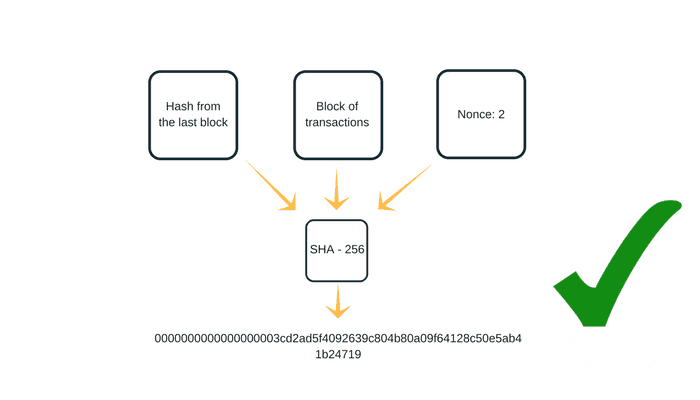
The original approach utilized by most digital currencies is called Proof of Work, in which’miners’ solve a mathematical problem, which in turn gives validity to a transaction. These problems are hard and do require a lot of computational power. A miner successfully solves the problem, adds a new block to the blockchain network, and, as a result, receives a monetary reward in the form of cryptocurrency.
The process ensures the security of the blockchain because solving such puzzles requires a lot of time and energy. Overpowering the network and changing transaction data requires enormous resources by any bad actor. This is the reason PoW is among the highly secure systems utilizing this consensus algorithm, though it normally comes with a handful of drawbacks.
The Energy Challenge of Proof of Work
The most critical problem with PoW is that it highly consumes energy; it requires high computer power to run 24/7 with high consumption of electricity. As the difficulty in solving problems grows, the energy consumption does, too, to maintain the network.
This has created concerns regarding the environmental impact of all cryptocurrencies, and also Bitcoin in particular. An example can be mentioned here that the power consumption of the Bitcoin network is compared to the power consumed by whole countries. In the light of an increasing emphasis on sustainability in the world, this challenge has created doubts as to whether Proof of Work is sustainable for a long period of time.
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake, on the other hand, is a significantly more energy-efficient consensus algorithm. There are no miners in a PoS network, but instead, it has validators. Validators are elected to mine the next block based on the number of cryptocurrencies that one owns and is willing to “stake” or collateralize. Further, they confirm the transactions and add a new block to the blockchain network.
Because computational processes that require enormous energy are not needed, Proof of Stake uses much less electricity compared to Proof of Work. As a matter of fact, greener alternatives, hence projects considering reduction of carbon footprint, find it appealing.
Security in Proof of Stake
While PoS is more energy-efficient, it is less secure, according to some, compared with PoW. The cost for the attackers in PoW is greater since there is a great deal of energy and computational resources involved. Meanwhile, PoS depends mainly on the amount of cryptocurrency staked by validators. When some validator acts maliciously, he loses his stacked coins.
Others argue that PoS will result in inevitable centralization because the majority of the network would be dominated by a few rich validators. That said, many experts feel that PoS, if complemented with measures for security, can be a sound security model besides being more environmentally friendly.
Pros and Cons of Proof of Work
Pros:
Highly secure because of the difficulty of solving cryptographic puzzles.
Has a proven track record, having been used by Bitcoin and Ethereum before its transition to PoS.
Cons:
Energy-intensive, hence high consumption of electricity.
Slow transaction speeds since miners must solve complex equations
Proof of Stake Pros and Cons
Pros
Much less energy-intensive, hence much greener
Faster speeds because complex puzzles do not have to be solved
Lower the entry barrier since participants don’t need expensive hardware.
Cons
A few concerns over security compared to PoW.
It also has some centralization issues whereby a few selected validators have the majority in power.
Still somewhat new when considering the long history of Proof of Work.
The Future of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
Which will power the future of crypto—proof of work or proof of stake? Well, this may not be a black-and-white answer.
With well-established networks, such as Bitcoin, Proof of Work is most likely to remain the standard since it has proven to be secure and resilient. However, Proof of Stake recently has been gaining momentum, especially in newer projects. Many projects today strongly focus on sustainability.
Ethereum is the second most popular cryptocurrency and made headlines in 2022 when it made the switch from PoW to PoS. The changeover, known as “The Merge,” was supposed to make Ethereum more energy-efficient and better scalable. Other blockchain networks have opted for PoS, such as Cardano and Polkadot. Both blockchains have thus received a significant dose of attention and popularity.
Will Proof of Stake Overtake Proof of Work?
In the future, it’s possible that Proof of Stake might take over as the main consensus mechanism. Its low energy consumption and faster block times make it a very attractive option for many developers and investors. Moreover, by making the security guidelines much more robust, blockchain technology is evolving rapidly.
Yet, Proof of Work is not going away anytime soon. For instance, Bitcoin’s network is inextricably linked to PoW, and many believe it’s too decentralized and secure to merit a move toward PoS. Rather, what we see might be a future in which both systems coexist, each serving different purposes and projects in accord with its peculiar needs.
Hybrid Models: A Middle Ground?
Some are working with hybrid models, which are, for instance, a mix between proof of work and proof of stake. Such systems attempt to give priority to the good of both worlds: retain a high level of security and consume less power simultaneously. For example, some networks, like Decred, use PoW for mining and PoS for governance—a well-balanced approach.
These hybrid models perhaps offer a vision of what the future of blockchain could be. Holding the strong points of both PoW and PoS in their implementations, they would probably answer some of the important questions that each system currently faces.
Conclusion
The debate cuts both ways: proof of work versus proof of stake. Each system is assigned different benefits and different challenges, and both will most likely play a considerable role in how blockchain develops in the future.
While Proof of Work is still an extremely secure and reliable solution, the environmental effects of it can no longer be neglected. On the other hand, Proof of Stake is a greener and more scalable alternative, but there are still security and centralization concerns that are yet to be overruled.
Ultimately, the future of crypto may not be a question of which system reigns supreme but how to strike a balance between the comparative strengths and weaknesses of each. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, both Proof of Work and Proof of Stake will arguably always coexist, powering different networks in ways that meet their unique needs.